- Who trades options and who futures?
- How to trade both methods?
- Can you make money trading futures options?
FX is one with many possibilities for you to make money. Options and futures trading allows you through leverage to manage more money and maximize your profits.
In this article, we’ll explain the basics of options and futures trading so you can start operating in these markets and make more money. Let’s start with basic definitions for each tool for better understanding.
What are the options?
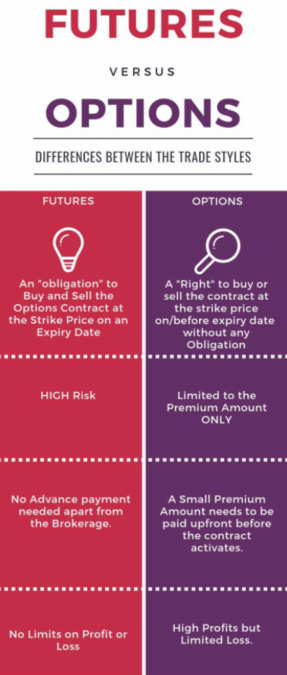
While buying or selling options, you are trading the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a lot of a pair according to the currency’s price in the specified period.
The critical elements of an option are the strike price, the time frame, and the premium. The point of an option is to transfer the risk to another party willing to accept that risk to pay a premium.
The strike price triggers the transaction because it can be exercised by the buyer when the currency’s price reaches the strike price within the specified time frame.
What are futures?
They are contracts used for the parties to protect themselves from market volatility. For example, when buying a future, a trader is obligated to buy the base currency and sell the pair’s quoted currency, and the other party has the opposite obligation.
As with options, the contract has an expiration date, but none of the parties pays a premium because they are both taking risks.
The extent of profit or loss varies. It depends on the difference between the agreed price and the actual price of an asset when the contract expires.
Who trades options?
Market participants who want to manage the risk of their investments often trade with options. In the case of options, there are two sides to the trade.
- One party wants to minimize the risk (the buyer).
- The party is willing to accept the risk of paying a premium (the seller).
Who trades futures?
Market participants who want to manage the volatility of the market often buy futures. For example, a trader who thinks that the EUR/USD will rise from 1,1789 to 1,1800 in the next 30 days may be attractive to buy a future to trade the pair EUR/USD at 1,1794. So, even if he is wrong, his loss wouldn’t be as big as if the price goes to 1,1800 and he didn’t purchase the contract.
How to trade futures?
The same principles used in FX trading can be applied to the futures market. Every trader wants to buy when the price is rising and sell before it goes down. The most important thing is to follow the trend to maximize your profits. That’s why next, we’ll talk about how to trade bullish and bearish trends.
Bullish trends
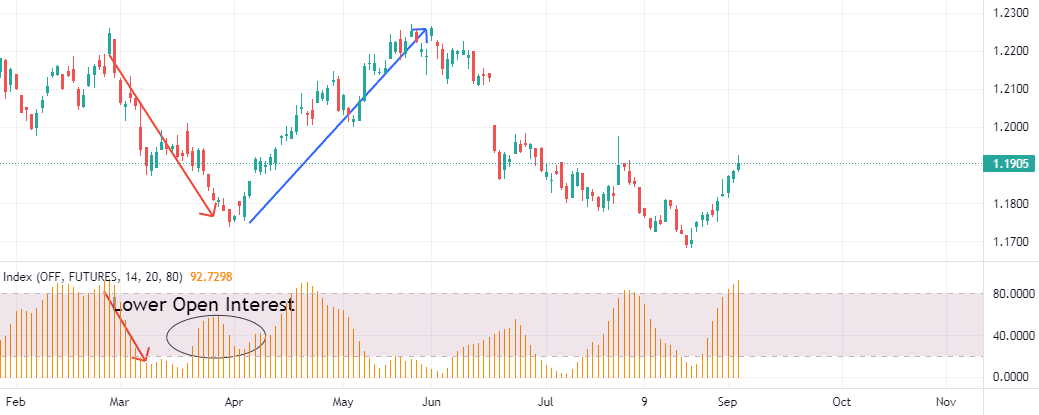
When we are about to face an uptrend, we want to enter a long position. Like in any other market, we want to be sure that our predictions are right. In the futures market, it is common to use the open interest indicator to confirm a trend.
Where to open?
When the futures contract price rises and the open interest indicator rises, this indicates a bullish trend. Here we buy contracts.
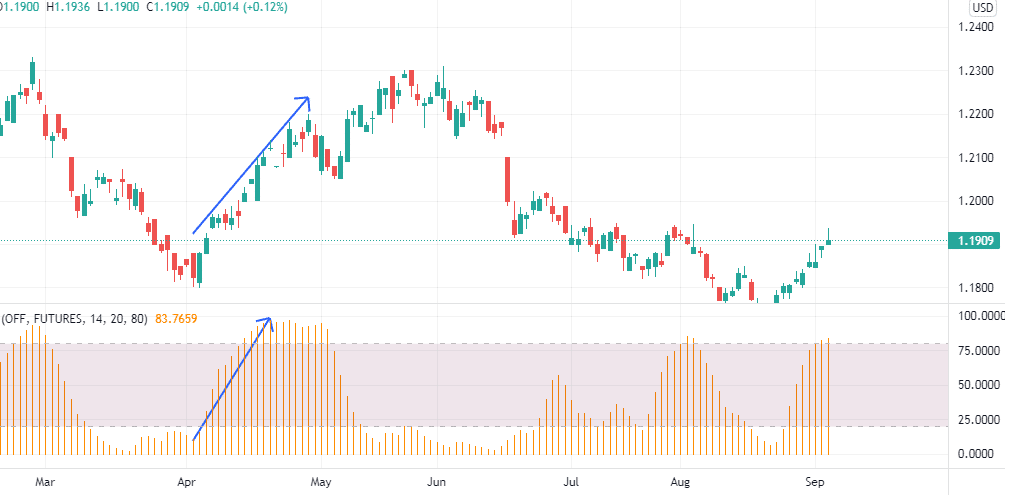
The image shows how the open interest indicator confirmed the trend, and it would be a wise decision to buy futures. However, it’s equally important to close a position when a trend pauses as it’s key to know the entry point.
Where to close?
If the open interest starts to flatten after a bullish trend where both the price and the open interest were rising, this is an indicator that the trend will stop and the price will reach its top. Then, it’s time to close the trade.
Flatten open interest
Bearish trends
On bearish trends, you enter a short position. So let’s see how the open interest indicator can help us to follow the downtrend.
Where to open?
We have a bearish sign when the prices and the open interest decline because long positions holders are discouraged.
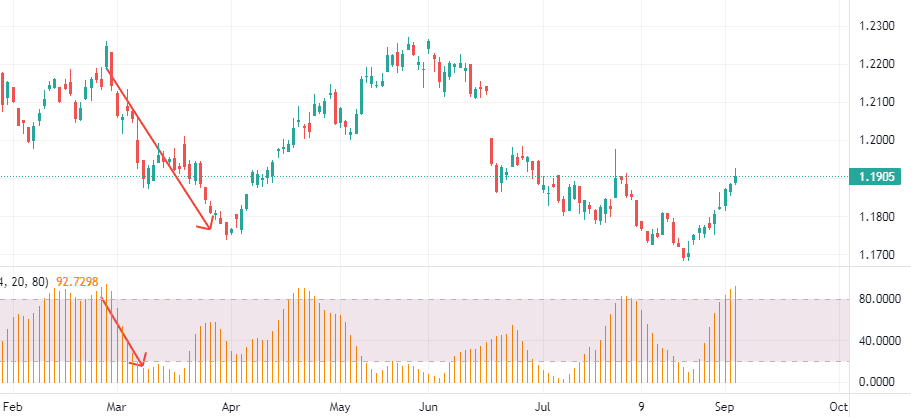
Where to close?
After the open interest stabilizes at a lower level, the liquidation from the long-position holders will be over, and the trend will reverse to go up again.
How to trade options?
Due to an option being a prediction on whether the currency pair’s price will rise or not, the first thing we should know is the trend’s direction. Since we are interested in the long-term trend, using Heikin Ashi candlestick patterns is appropriate.
Bullish option
We want to enter a long position for the bullish option and sell it before the price downtrend.
Where to open?
We’ll open a position once we confirm that the price will continue the uptrend. In the following example, we use a Heikin Ashi candlestick pattern to predict that the price will rise.
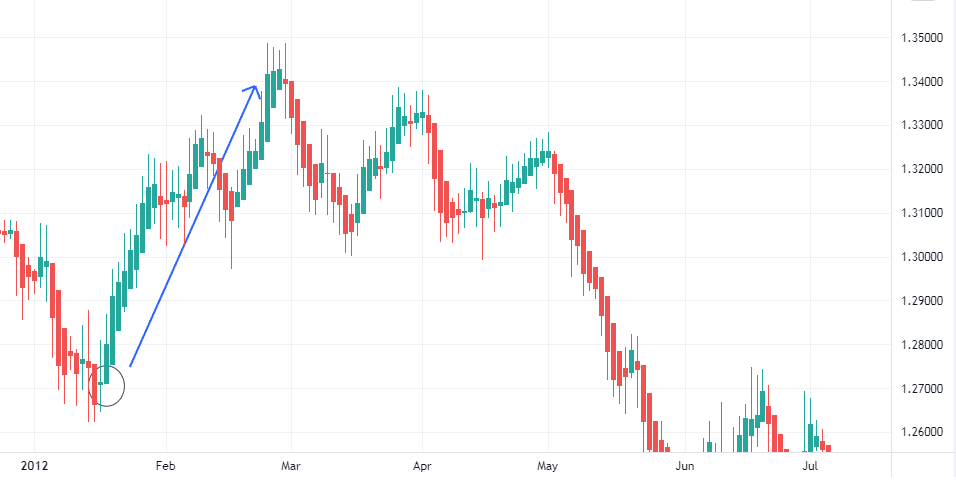
We see in the circle, after a downtrend, there is a Doji candlestick that predicts a reversal, and the candlesticks next to it, confirm the uptrend.
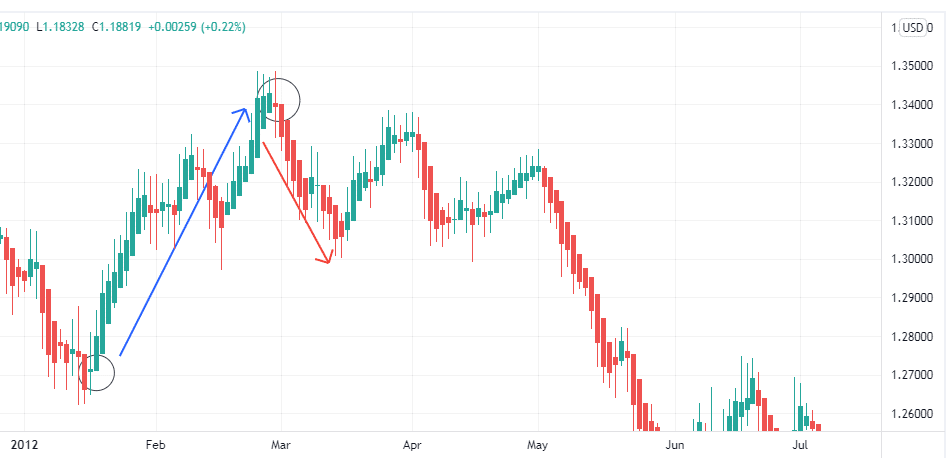
Where to close?
The end of the trend is also given by a Doji, indicating the reversal of the trend. This is the moment to exit the position.
Bearish trends
We want to either sell a call option to earn the premium or buy a put option for the bearish trend. Here Heiken Ashi candlesticks are also useful.
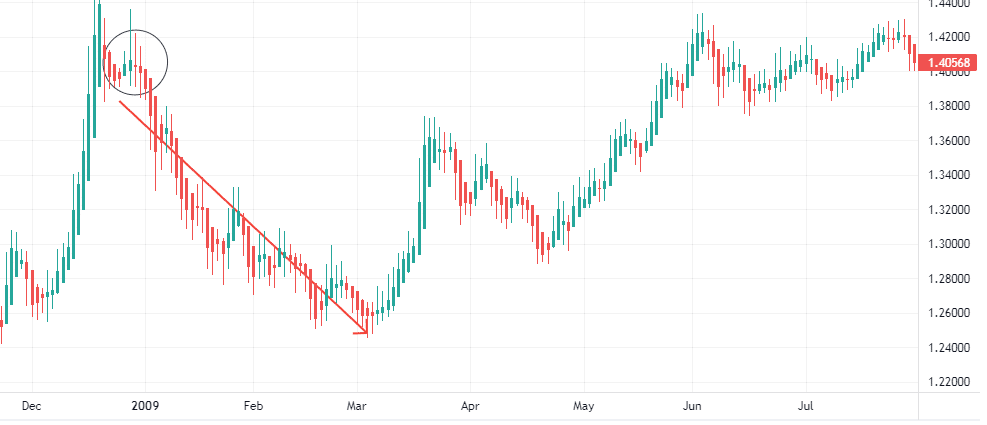
Where to open?
After an uptrend, the Doji candlestick again indicates a reversal in the trend, and the next few candles also point down, confirming the downtrend.
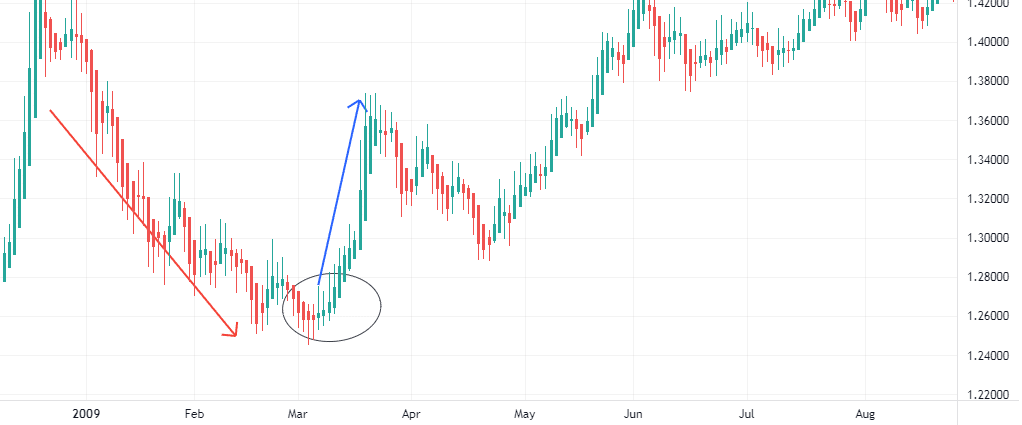
Where to close?
Although we see some minor reversal along the way, the pattern in the circle indicates the right moment to exit the position. In the circle, we see how the bearish candlesticks are weaker, and the following bullish candlestick consistently forms an uptrend until the trend is strong with long candlesticks.
Options on futures
There is still another layer on the futures and options trading market, option on futures. The option on futures gives the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy/sell a futures contract. Thus, whoever applies this strategy gets the best of both trades: risk management from options and the hedge of futures contracts.
Final thoughts
Futures and options are agreements to trade currencies in a specified period in the future. The difference between the two is the obligation to comply with the agreement. While in a futures contract, both parties are obligated to make the transaction, with options, the buyer pays a premium to exercise the right to make the trade only if he desires to.
Thus, the main advantage of futures is to get a hedge while options are meant to manage the risks.