- How do you read the stock market?
- How does the stock market work for beginners?
- How can you understand this market and invest?
Stock market investing is one of the best ways to build net worth. While you can build wealth through savings, inflation will reduce the buying power of your money in the years to come. In contrast, stock investing provides great returns to combat inflation.
Of course, there are risks involved in stock market investing. Buying stocks is better when the markets are in a downturn. But if you still bought on highs, it doesn’t matter; any market crisis will sooner or later be replaced by growth.
True, sometimes you have to wait a long time. The most prolonged recession in the US stock market happened in 1929 and lasted 43 long months. The next most prolonged recession occurred already in this millennium, the crisis of 2007-2009, which lasted “only” 18 months.
Let’s learn some stock market basics, which can be a starting point in your stock investing journey.
What is stock?
Otherwise known as equity, a stock is a security that constitutes an investor’s ownership of a portion of a business or corporation. Owning a stock qualifies you as an owner of a particular piece of the assets and profits held by a corporation. The percentage you own depends on how much stock you hold. Each unit of stock is termed a share.
Publicly traded companies issue shares to investors that can count to millions or more. For example, if you own 200,000 shares of a corporation that issued four million shares, you will have a five percent stake in the corporation. To get the actual percentage of your stock ownership, divide the number of shares in your possession by the total number of outstanding shares.
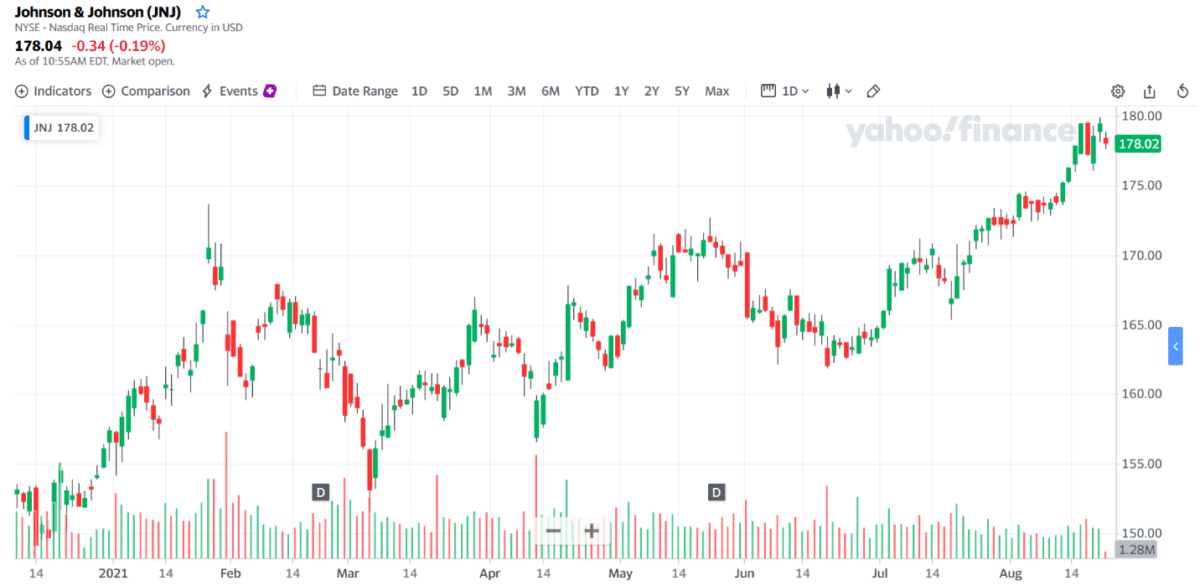
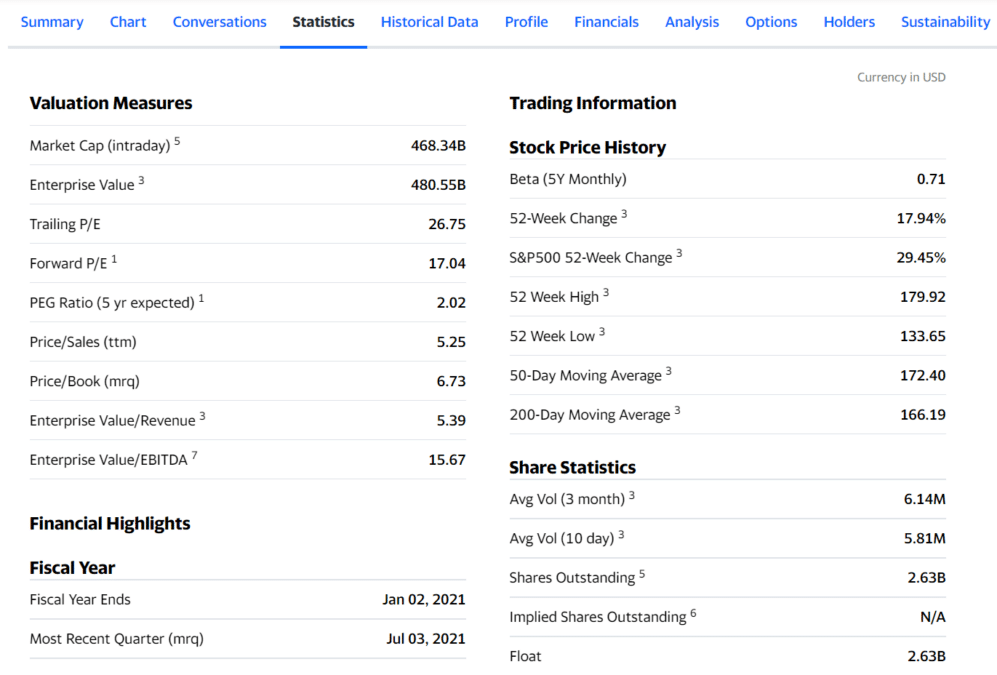
Let us take Johnson & Johnson as an example. The first image above is the daily chart of this stock at the time of this writing. This stock offers 2.63 billion outstanding shares, as you can see in the second image.
Two kinds of stocks
There are two main variants of stocks:
- Common stock
- Preferred stock
If you have heard about the term “equity,” what it means is common stock. In comparison to preferred stock, common stock is dramatically more enormous in trading volume and market cap.
The main difference between the two shares is voting rights. The common stock allows its shareholders to participate in corporate meetings and voice board members’ election, selection of auditors, mergers, etc. Generally, preferred stock shareholders do not have such rights. The qualifier “preferred” means that these shareholders are preferred over the common shareholders when receiving dividends and assets in case the company at issue is subject to liquidation.
In common stock, voting rights may vary depending on classification. The basic variety may entail one vote per share, but a higher classification may mean ten votes per share. The actual number of votes varies from one company to another and the number of categories. Multiple varieties are put in place to allow the founders to drive the strategic direction of the company.
Why do companies issue shares?
Big corporations today might have started as small private companies in the past established by visionary founders. Consider Alibaba, for example. Jack Ma started it in 1999 in his apartment in China. Another example is Facebook. Mark Zuckerberg established it in 2004 from his dorm room at Harvard University. These two companies are prime examples of technology giants that turned into household names in a couple of decades.

Lifting a company from the ground and accelerating its growth requires a huge amount of capital. To bring an idea to reality, someone must lease a space, purchase equipment and materials, and hire employees. If you happen to own that business, you need to pool a large amount of capital to push your business to greater success. You can raise such capital through the process of initial public offering (IPO).
Raising capital
To raise capital, a startup can use IPO or debt financing (i.e., borrow money). Startups might struggle with debt financing because they may not have enough assets to be used as collateral. This is particularly true for companies operating in the biotechnology or technology sectors.
In the early days of the business, it might not generate enough profit to pay for the periodic principal payment plus interest on the loan. Therefore, most startup companies turn to venture capital firms and investors to acquire more capital to expand their business.
Listing shares
As a company grows and stabilizes its business operations, it might need more capital than a traditional bank loan, or business profits can offer. The company can source this capital by issuing shares to the public in an IPO. So this elevates the stature of the corporation from a private entity to a publicly traded company.
Only a few shareholders hold the shares; in the latter, investors have many of the shares. At the same time, investors who came in during the nascent days of the company may take out a large portion of their returns during the IPO, and they can get hefty rewards at this point.
After a while, the company will have its shares listed and traded on a stock exchange. As traders and investors trade the stock, the share price will rise and fall depending on how the participants perceive the value of the stock. You can use various metrics to value a stock. The most widely used is the price-earnings ratio. Speculators may use fundamental or technical analysis, and both when assessing the short- or long-term direction of the stock.
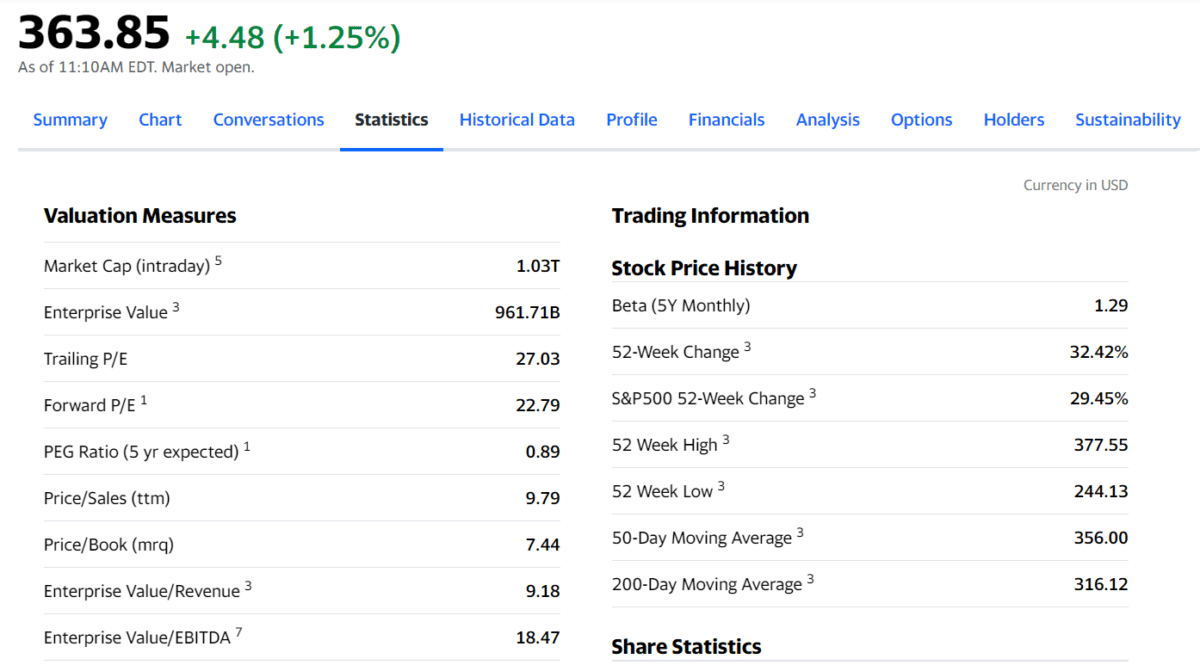
Let us consider the current price-earnings ratio of Facebook. The above image shows the current and future ratios as 27.03 and 22.79, respectively.
How are share prices set?
The most familiar way is through a bidding process where market participants offer to buy/sell orders.
- Ask price is the price set by traders looking to sell a stock.
- Bid price is the price set by traders looking to buy a stock.
A trade occurs when the ask and bid prices correspond. Millions of traders and investors make up the stock market, and these participants may assign different values to a certain stock. They may have other preferences as to the price they would like to buy or sell this asset. The buying and selling behavior of a collection of these market players results in thousands of trading transactions that cause price fluctuations every minute throughout the trading day.
You can make transactions in a stock exchange, a platform that matches buyers and sellers to facilitate trades. If you want to access an exchange, you need to connect to a stockbroker, an intermediary between buyers and sellers.
Final thoughts
What you have learned here is just a basic introduction to the stock market. Now you have more understanding about the stock market, such as the types of stock, the purpose of issuing shares, and how exchanges generate trade transactions. You need to get more information somewhere before you can start your stock investing journey.