- What is investing in stocks?
- What is investing in bonds?
- What to know before investing?
There has been a significant increase in the number of people investing in securities over the past few years. Investing in stocks and bonds is the most traded investment asset, as you may already know.
In New York City, Stacy Francis, the president and CEO of Francis Financial, divides long-term investing into three categories, depending on your target date for the goal:
- up to 15 years
- 15 to 30 years
- more than 30 years
According to Francis, it makes sense to invest conservatively with the shortest timeline, with 50% to 60% of the portfolio in stocks and the rest in bonds. At the most aggressive level, the investment allocation could reach 85% to 90%.
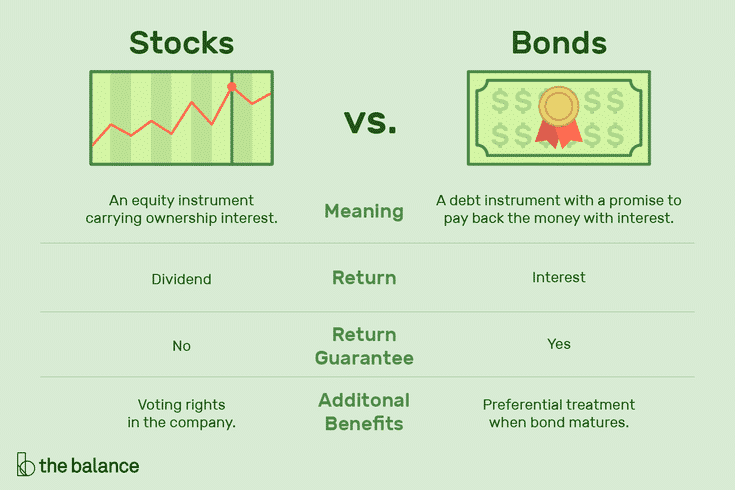
If you’re a novice investor, your first question might be, what is the difference between stocks and bonds? This article compares these two tradable assets, explains which one performs better and which one is safer. You could improve your investing skills if you understand how stocks and bonds work. So, to understand both of them, let’s explore them.
What is investing in stocks?
Stocks are equity investments or shares. They represent part ownership in the form of shares in a publicly-traded corporation. In exchange for their partial ownership rights, investors earn when the company performs well.
The earnings may additionally be distributed as dividends. In most cases, companies will use the retained earnings to expand operations or to acquire strategic companies. Some companies, on the other hand, choose to keep a portion of their profits. Consequently, they will earn higher profits in the future.
Generally, investors prefer stocks since they have a high chance of long-term success. For a company to profit, it must perform well. As its shareholder, you share in their success.
In addition, their prices are influenced by many factors. Company performances affect the price, for instance. But, on the other hand, the company depends on its environment-its, customer, industry, economy, and political environment.
A distinction must be made between investing and speculating. Speculating is the process of purchasing equity in a company that isn’t making a profit.
Those with experience understand the importance of the last one. It would help if you always did some research on the company before buying stocks from it. This should be done before investing in the company, too.
Examining its income and balance sheets, annual reports, and reputable equity investing publications and websites is essential.
| Upsides | Downsides |
| An equity instrument with ownership interests. | Returns on capital are not guaranteed. |
| Exceptional return potential. | It is risky to invest in stocks. |
| Taking part in the company’s ownership. | There is no guarantee that dividends will be paid. |
What is investing in bonds?
In a nutshell, these are fixed-income loans with a security element. Bonds typically have a fixed return as well. A repayment date will also be set for the loan amount in the future.
In addition, the bond issuer is referred to as the borrower of the bond. Meanwhile, investors are called bondholders. A bond pays a predetermined interest rate, known as the coupon, at predetermined intervals to repay the principal on the maturity date, thereby wrapping up the loan. The coupon tends to be paid annually.
Thus, bonds are securities whose issuer is required by law to pay specified interest and principal to their holders on selected dates. Therefore, a bond issuer pays interest every period, but the principal will not be repaid until the loan is repaid.
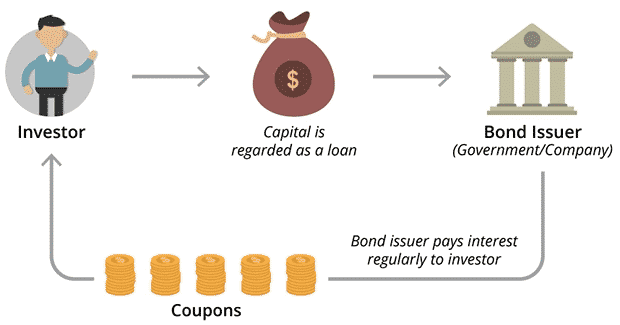
A corporation or a government typically issues a bond. Therefore, it is regarded as a safer investment than shares. There are several kinds of bonds to suit different needs of investors, including corporate, Treasury, Agency GSEs, municipal bonds, etc. Furthermore, bondholders in some countries are protected by law. Therefore, it may be possible for bondholders to receive money if a company goes bankrupt.
According to statistics, these also have lower volatility than shares. Not only that, but sometimes it makes higher interest payments than the general dividend payout level. Furthermore, bond prices tend to rise when rates drop and vice versa. Conversely, when rates increase, bond prices drop.
| Upsides | Downsides |
| The bond will also receive preferential treatment upon maturation. | The volatility of makers. |
| At maturity, interest repayments and principal are due. | Low returns compared to stocks. |
| Volatility is lower than stocks. | The yield on the bonds can fall. |
What to know before investing?
1. Stocks are a riskier investment than bonds
Bonds offer a higher repayment priority than stocks, making them a riskier investment. In contrast, bondholders may be given a much higher priority. As an example, shareholders would be entitled to any leftover cash in a business liquidation.
2. Stockholders have voting rights
Bondholders do not have a vote when company issues are discussed. Stockholders, however, can vote when company issues are discussed.
3. Bonds are less volatile
Due to the fixed rate of return on the bonds, bonds are less volatile. Consequently, bonds are viewed by many investors as a safer investment than stock. However, several factors contribute to volatility, such as expected inflation, discount rates, and present rates.
4. Some bonds have conversion features
According to the terms of bonds, some bonds have conversion features. Thus, bondholders can convert their bonds into company shares. Investors who know how to use this tool know its usefulness, especially when its stock prices rise.
By converting their bonds into company shares, bondholders can reap the benefits of capital gains. In addition, as mentioned earlier, by doing this, bondholders will have the right to vote on certain company matters.
5. Stocks provide greater return potential = increased volatility = greater risk
The resale of them is easier because they are liquid.
Final thoughts
The aim of investing is to build an investment portfolio with diversified assets. Diversification is typically characterized by maintaining a portfolio with a variety of assets. An investor’s portfolio becomes more diversified the more stocks and bonds they own.
Using this method, you can reduce your portfolio’s risks and volatility over time. However, it’s essential to understand that diversification doesn’t guarantee you will win or won’t lose. As a result, investing in stocks and bonds always involves surprises. So, it would help if you manage your risk wisely.