- When should a trader use a Box spread?
- Is it a profitable strategy?
- Is this strategy low in risk?
Box spread is a primary notion from options trading. It needs a particular number of payouts to develop an impartial interest rate market position. Thus, traders input their position as it involves buying a bull or long call spread also, hedging as it is the opposite of a matching bear or short put spread.
Thus, the Box spread is alluded to as an arbitrage strategy that market participants enter buying a call spread together with a put spread. The net payout of this method is the deviation between both spreads. All of the transactions or trades necessitate a commission. In the same way, there is a commission charged in Box trading. It is supremely significant to consider the commission while reaching a profit by entering.
Let’s watch buying and selling methods on this strategy.
What is a Box spread?
It is a 4-leg option strategy that includes two strikes and consists of:
- Debit call spread
- Debit put spread together with similar strikes.
Likewise, a short Box spread consists of a credit call spread and credit put spread along with the identical strikes.
In a broader meaning, such spread is an arbitrage strategy, a combination of buying a bull call spread along with a matching bear put spread. It is imaginable as two upstanding spreads, each having similar strike prices and validity. However, Box spreads are utilized for scrounging at the unstated rate, which is more flattering for a trader instead of going to a clearing firm, prime broker, or any bank.
Since the price of a Box with validity will be the difference between the involved strike without any exception. The paid price for today is considered a zero-coupon bond. If the primary price of the Box is low, the unstated interest rate will be higher, which is counted as per the synthetic loan concept.
How to use it in the crypto market?
The method is impeccably utilized, while the spreads are underrated concerning their validations values. The trader may take on a short Box if they feel the spreads are overrated utilizing the contrary options pairs. Also, while one considers the motive of the two upstanding, which is a bull call and a bear put involved in a spread, the theory of the Box becomes apparent.
Moreover, while the fundamental asset closes at the higher strike price at expiration, a bullish vertical spread accelerates its net profit. Conversely, while the fundamental asset closes at the lower strike price at expiration, a bearish vertical spread amplifies its net profit.
Since the payout will be the deviation between the two strike prices at expiration without exception, the trader removes the unknown by conjoining a bull call spread and a bear put spread.
As per the delta-neutral method, the trader may lock a risk-free profit if the spread cost is less than the deviation between the two strike prices after the commission. Contrarily, the trader may encounter a loss only, including the execution cost of the strategy.
Short-term trading strategy
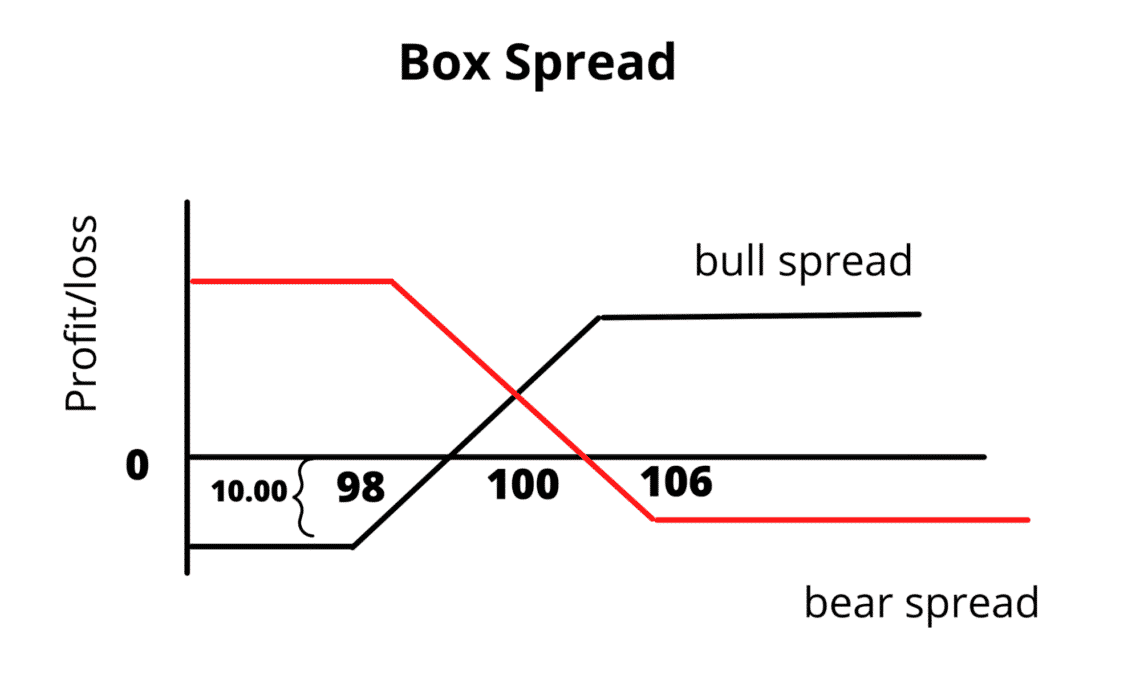
Let’s say a financial trading instrument is trading at $100. Each option contract consists of ten units of the trading instrument. Therefore, the short-term method approach should be as follows:
- Buy the 98 call for 3.29 (ITM) for $3224 debit per options contract
- Sell the 106 call for 1.23 (OTM) for $1303 credit
- Buy the 106 put for 2.69 (ITM) for $2851 debit
- Sell the 98 put for 0.97 (OTM) for $950 credit
In that case, the commission for the trade should be as follows: $3224 – $1303 + $2851 – $950 = $3822. The spread between these prices is 106 – 98 = 8. Now multiply by ten units = $800 per Box spread.
Long-term trading strategy
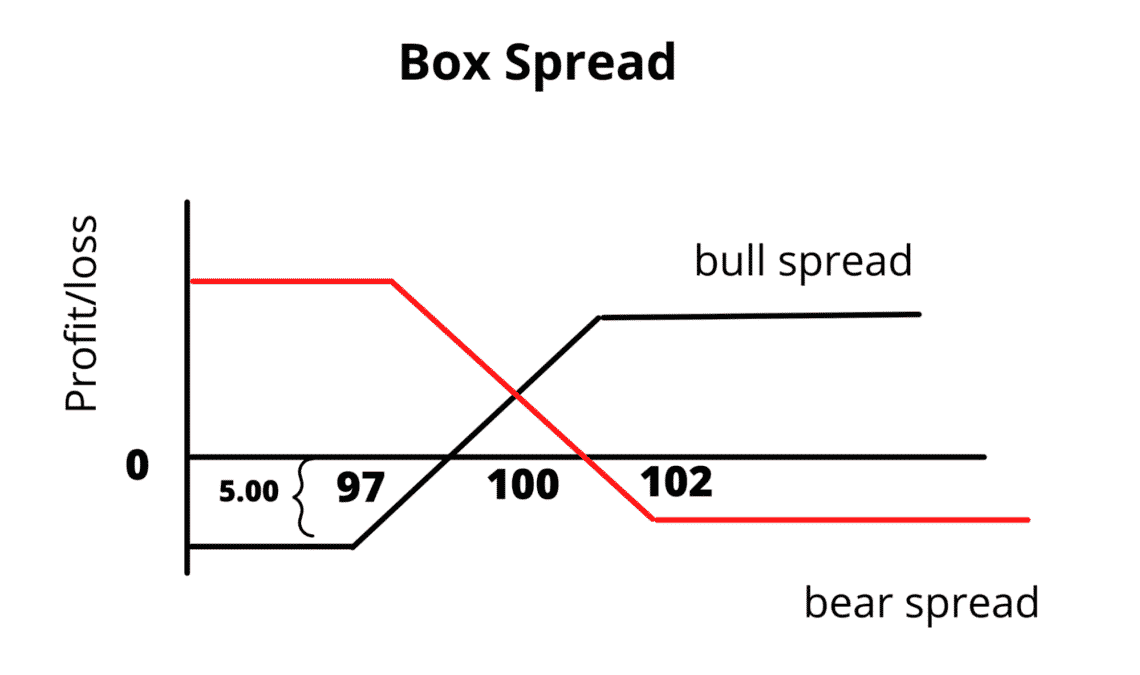
Let’s assume that an options trading instrument is trading at $100.
- First “in-the-money” call option at the strike price $97 for $5 a share
- Second “in-the-money” put option at the strike price $102 for $5 a share
- Third “out-of-the-money” call option at the strike price $102 for $3 a share
- Fourth “out-of-the-money” put option at the strike price $97 for $3 a share
In that case, the overall cost should be $4 (5 + 5 – 3 – 3 = 4). In that case, if the trading instrument closes the day at $100 in a month, the “in-the-money” will be executed and the overall process will close with $1 profit per share (5 – 4 = 1).
Pros & cons of the Box spread
| Pros | Cons |
| It helps to generate small profits but with zero risk. | This method is not suitable for retail traders. |
| You may take money in a short Box without tying up the capital. | Due to its high margin maintenance requirements against the available margin, traders do not find it appropriate to trade with the strategy in most cases. |
| It is suitable for professional market participants as it is supervised with a high-frequency algorithm. | The strategy only sounds good theoretically, but the reality is that it can only earn small profits. |
Final thoughts
This strategy is beneficial to the market participants intending to generate a risk-free small profit. Due to its high-frequency algorithm, the technique demands higher expertise in implementing the method and profit. Therefore, mostly master traders are willing to execute the strategy. Significantly, the key to generating profit from the method is the vital timing in utilizing the system.