- What is options trading?
- Which are the best strategies?
- How to make more money on them?
This trading type is one of the favorite tools for market participants who want to minimize risks. By purchasing an option, the trader transfers the risk to another party for a premium.
Some of them are so liquid that they trade with a one-cent spread, just like the underlying stock. They can even be speculated within the day using considerable option leverage. And there are options for which not a single transaction takes place during the day. But the market participants can trade such options in large volumes since market makers will consistently execute your order.
With simple options trades, it’s the seller who takes almost entirely the risk. But there are many ways for the seller and the buyer to improve their risk to reward ratio.
Let’s see the top ten strategies.
What is options trading?
It’s a market where traders sell and buy the right but are not obligated to execute a trade when the conditions are met.
There are two types of them: call and put. By purchasing any of these two, the buyer protects from price movements against him while the seller tries to profit from his premium.
Why are strategies necessary in options trading?
Here strategies are designed to protect us from price movements against us. They combine two or more assets to compensate for the losses of one option.
Which are the best?
Let’s explore the top ten types that may benefit in your live trading.
1. Married put
This strategy has the purpose of protecting the long positions of the investors who use it. It consists of two movements:
- Enter a long position for the pair the trader wants to own.
- Buy a put option at-the-money or out-of-the-money.
If the currency price falls, the trader is protected by the put option, which gives him the chance to sell the currency at the strike price.
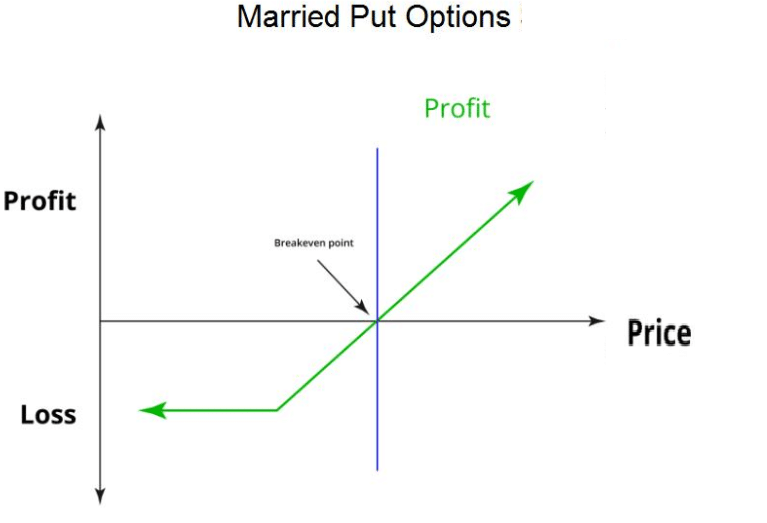
Risk/Reward
The maximum risk of this strategy is to lose the premium by not exercising the put option. On the other hand, the reward is unlimited since there is no limit to the price of the bought currency.
2. Covered call
It is a strategy in which the trader sells a call option for an underlying asset he already owns. Thus the seller is betting that the price won’t rise to a certain level, and he will keep the money from the premium. The steps for making a covered call are:
- Enter a long position for the pair the trader wants to own.
- Selling a call option at a high strike price.
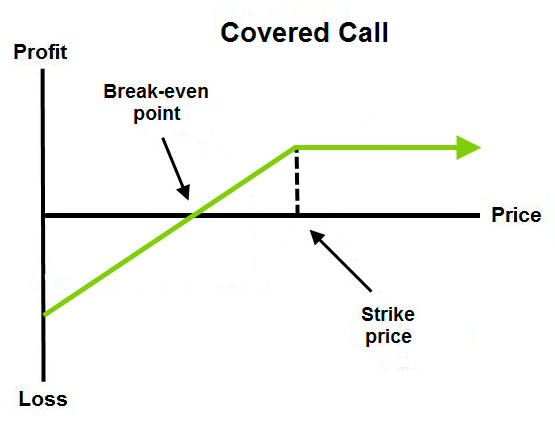
Risk/Reward
The currency price could rise unexpectedly, and the trader would be obligated to sell at the strike price, so the risks are unlimited. However, the max reward is obtained when the price doesn’t reach the strike price, and the seller of the option gets to keep the premium.
3. Bull call spread
It is used when the trader thinks the price will continue to uptrend moderately in the short term. It consists of two simultaneous movements:
- Buying a call option at a certain strike price.
- Selling a call option at a higher strike price.
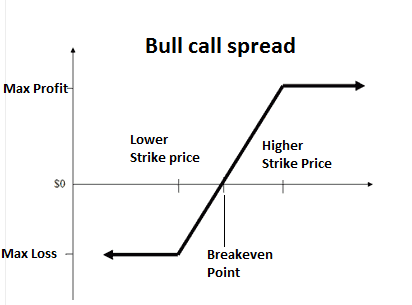
Risk/Reward
The risk for this strategy is limited to the premium paid minus the premium received, and it occurs when the pair price is lower than the strike price for the bought call.
The max reward is also limited and is achieved when the currency price reaches the strike price of the written call.
4. Bear put spread
It is a strategy for traders who think that the price of the underlying will downtrend moderately or largely in the short term. The way of setting the strategy is:
- Buy a put option.
- Sell a put option with the same parameters as the put bought but with a lower strike price.
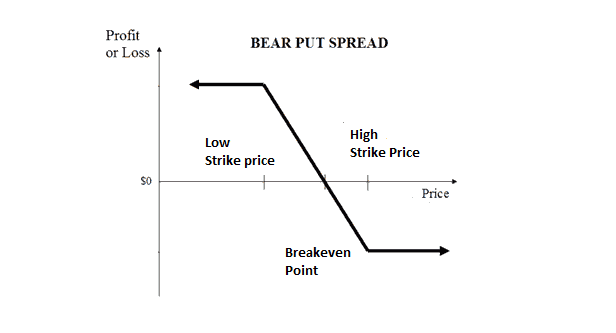
Risk/Reward
The risk for this strategy is limited to the premium paid for the bought put option. The max profit is also limited and is equal to the difference between the two strike prices. The reward is achieved if the price stays below the strike price for the written put option.
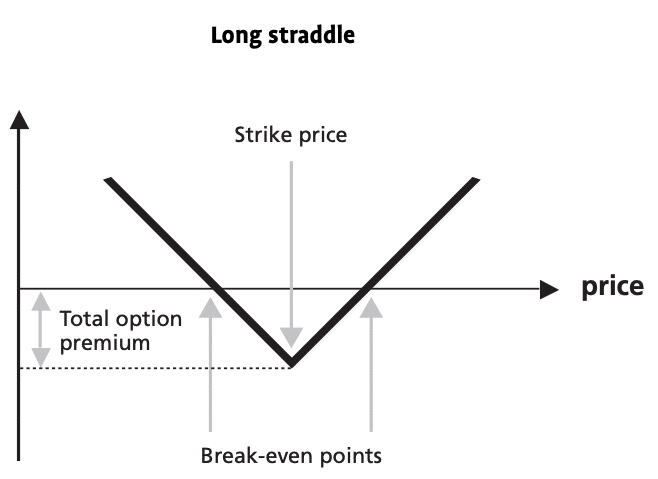
5. Long straddle
It’s used when we expect an increase in the volatility of the price. It consists in purchasing both a call and a put option with the same strike price. So here, the trader is betting that the price will move largely in any direction. The movement has to be big enough to compensate for the payment for the two premiums. The way of setting it is:
- Buying a call option at-the-money.
- Buying a put option with the same parameters.
Risk/Reward
The risk for this strategy is limited to the sum of the two premiums paid. The reward is unlimited if the price rises and is significant if the price declines because the lowest possible price is zero.
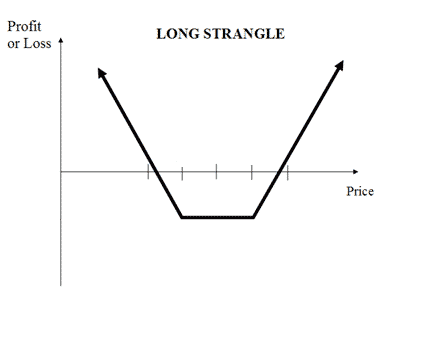
6. Long strangle 2
It’s similar to the long straddle with the difference that the options will be out-the-money. The advantage of this strategy is the lower investment on premiums because the options are slightly out-of-the-money. So the premium costs will be lower. Long strangle is used when the trader expects the price to move largely. The step for setting long strangles are:
- Purchasing a call option OTM.
- Purchasing a put option OTM with a lower strike price.
Risk/Reward
The risk is limited to the premiums paid for the two options. The reward is unlimited in case the price rises and significant in case the price declines to zero.
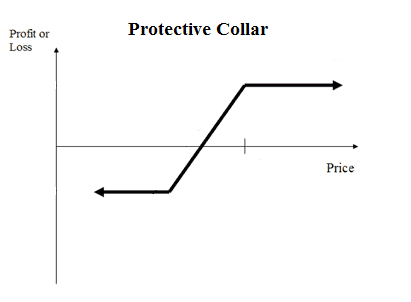
7. Protective collar
When a trader fears that his assets can lose value, using the protective collar strategy can be helpful to avoid losses if the price falls and even profit if the price goes up.
The way to apply this strategy is:
- Purchase a currency pair.
- Buy a put option out-of-the-money.
- Selling it with a higher strike price.
Risk/Reward
Both the risk and the reward are limited with this strategy. The max loss is equal to the difference between the pair price and the put strike price. The max profit is equal to the difference between the pair price and the call strike price.
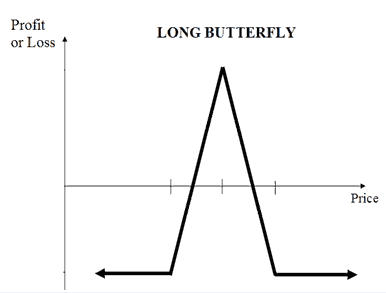
8. Long call butterfly spread
It’s an advanced technique that combines four different options and has limited risk and reward. The cost of this strategy is high due to the premiums and commissions paid for the options traded. The setup is:
- Buy a call option at a strike price X.
- Sell two call options at a strike price Y where Y>X.
- Buy a call option at a strike price Z where Z>Y.
Risk/Reward
The point of this strategy is to have both limited risk and reward. The maximum risk is the net cost of the strategy. The max reward is the difference between the strike price X and the strike price Y minus the net cost of the strategy.
9. Iron condor
We use this strategy when the trader believes that the price won’t move a lot, so it profits from the currency stability. The setup of it:
- Buy a put with a strike price A below the current.
- Sell a put with a strike price B below the current but closer to it than A.
- Sell a call with a strike price C above the current.
- Buy a call with a strike price D even further from the current than C.
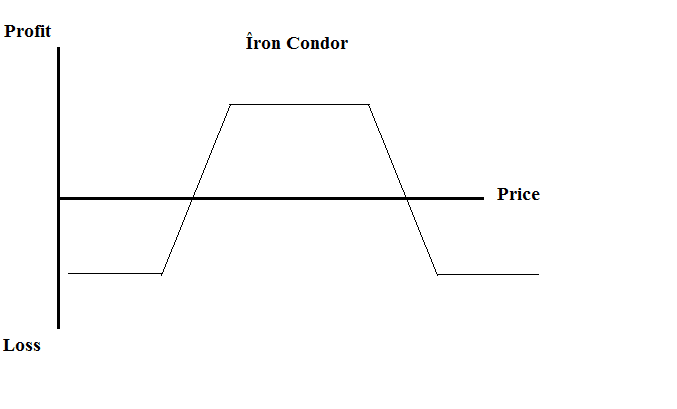
Risk/Reward
The maximum loss for the iron condor is limited by the difference between the strike prices of the bought call and the sold call. The max profit is the premiums collected by the options sold.
10. Iron butterfly
It’s the combination of four different options to profit from the price stability. The way of using the iron butterfly strategy is:
- Identifying a target price to which the trader believes the price could reach.
- Buying a call with a strike price far higher than the target price.
- Selling both a call and put near to the predicted price.
- Buying a put far below the expected price.
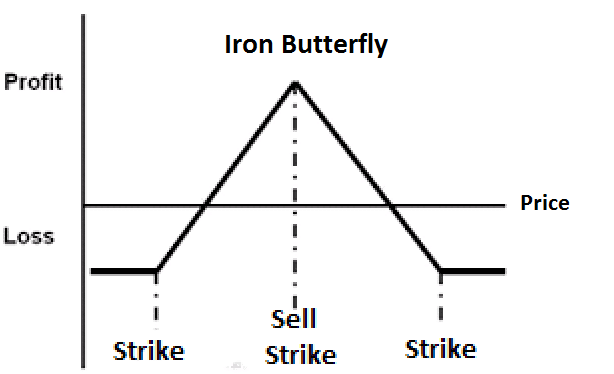
Risk/Reward
The maximum profit is the difference between the strike price of the bought put option and the options sold. Thus, the maximum profit is credit collected.
Final thoughts
These strategies allow you to make safer trades and manage more money thanks to leverage. Some of them are more complex, but they all have in common that we can use each to improve the risk to reward ratio.